
安全起见:相信关于增强性能力的传统知识,使用东革阿里
西方医疗机构和跨国制药公司诋毁草药。草药不符合医生的商业模式,因为它们不像危险药品那样需要处方,从而剥夺了医生的权力和诊费。由于草药不能申请专利(以防止竞争导致定价过高),它们当然也破坏了大型制药公司的商业模式。
草药与西药的区别在于,草药与包括人类在内的其他生命形式有着共同的进化历史,而大多数药品都是异生物制剂。虽然有些异生物制剂可以用来改善某些病症,但异生物制剂有 99.99% 的可能性会产生长期的有害影响。
低估长期不利影响是化学制药行业的常见现象。杀虫剂滴滴涕最初也被认为对人体无害。
这并不是最不恰当的诺贝尔医学奖。1949年,葡萄牙神经学家安东尼奥-卡埃塔诺-德-阿布鲁-弗莱雷-埃加斯-莫尼兹(Antonio Caetano de Abreu Freire Egas Moniz)因在精神病患者额头上钻孔(脑叶切除术)以使其安静下来而获奖。
最臭名昭著的美国外科医生是沃尔特-杰克逊-弗里曼二世(Walter Jackson Freeman II,1895 - 1972 年)。
Wikipedia 关于 Rosemary Kennedy: "罗斯玛丽开始在晚上偷偷溜出修道院学校。修道院的修女们认为罗斯玛丽可能与男人有染,她可能会感染性传播疾病或怀孕。她反复无常的行为让她的父母感到沮丧;她的父亲尤其担心罗斯玛丽的行为会让家庭蒙羞和难堪,并损害他和孩子们的政治前途...... 约瑟夫-肯尼迪决定让罗斯玛丽接受脑叶切除术;然而,直到手术完成后,他才将这一决定告知妻子... 很快,人们就发现手术并不成功。肯尼迪的智力下降到两岁儿童的水平。她无法行走或说话,大小便失禁。"
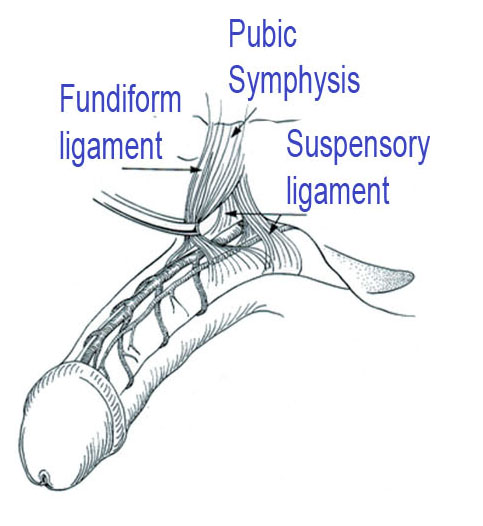
想在另一个珍贵器官上动手术吗?阴茎整形术?
请注意:选择性手术是那些开法拉利、计划买游艇的医生的首选领域。
市场上有各种阴茎增大手术。
何不稳妥行事: 相信传统的非侵入性增强知识,使用东革阿里。
Ang, H. H.; Ngai, T. H. (2001), Aphrodisiac evaluation in non-copulator male rats after chronic administration of Eurycoma longifolia Jack, Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology, Volume15, Issue4, Pages 265-268
Chaturapanich, G.; Chaiyakul, S.; Verawatnapakul, V.; Yimlamai, T.; Pholpramool, C.(2012),
Enhancement of aphrodisiac activity in male rats by ethanol extract of Kaempferia parviflora and exercise training, Andrologia, Vol 44 (Suppl 1), Pages 323-328
Chaipech, S.; Morikawa, T.; Ninomiya, K.; Yoshikawa, M.l; Pongpiriyadacha, Y.; Hayakawa, T.; Muraoka, O. (2012), Structures of two new phenolic glycosides, kaempferiaosides A and B, and hepatoprotective constituents from the rhizomes of Kaempferia parviflora, Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, Vol 60, Pages 62-69
Chen, Dalin; Li, Hongliang; Li, Wen; Feng, Shuo; Deng, Dingsen (2018), Kaempferia parviflora and Its Methoxyflavones: Chemistry and Biological Activities, Hindawi Journal, Volume 2018 |Article ID 4057456 | https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4057456
Chivapat, S.; Chavalittumrong, P.; Attawish, A.; Rungsipipat, A. (2010),
Chronic toxicity study of Kaempferia parviflora Wall ex. Extract
The Thai Journal of Veterinary Medicine, Volume 40 (4), Pages 377-383
https://tci-thaijo.org/index.php/tjvm/article/view/35774/29744
Chivapat, S.; Chavalittumrong, , P.; Attawish, A.; Rungsipipat, A. (2004),
Acute and chronic toxicity study of Kaempferia parviflora Wall ex. bak powder,
Journal of Thai Traditional and Alternative Medicine, Volume 2 (2), Pages 3-16
Deema P. (2007), Effect of Kaempferia parviflora and Endurance Training on Lactate Threshold in Humans Phitsanulok, Thailand: Naresuan University
Diastuti, Hartiwi; Chasani, Mochammad; Suwandri, Suwandri (2020), Antibacterial Activity of Benzyl Benzoate and Crotepoxide from Kaempferia rotunda L. Rhizome, Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, Vol 20, No 1
GG, Faisal; SM, Zakaria; GF, Najmuldeen (2015), In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Eurycoma Longifolia Jack (Tongkat Ali) Root Extract, International Medical Journal of Malaysia, Volume 14, No. 1
Girish, Sonal; Kumar, Suresh; Aminudin, Norhaniza (2015), Tongkat Ali (Eurycoma longifolia): a possible therapeutic candidate against Blastocystis sp., Parasites Vectors, Volume 8, Pages 332
Henkel R.R.; Wang R.; Bassett S.H.; Chen T.; Liu N.; Zhu Y. et al. (2014),
Tongkat Ali as a potential herbal supplement for physically active male and female seniors - A pilot study , Pharmacological Research,
Volume 28, Pages 544-550, https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5017
Hien, Dao Thi Thanh; Long, Tran Phi; Thao, Tran Phuong; Lee, Jeong-Hyung; Trang, Duong Thu; Minh, Nguyen Thi Thu; Cuong, Pham Van; Lan, Dang, Nguyen Hai; Dat, Nguyen Tien (2019), Anti-inflammatory effects of alkaloid enriched extract from roots of Eurycoma longifolia Jack, Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, Volume : 9 , Issue : 1 , Pages : 18-23
Hirsh, Steven; Huber, Luke; Stein,Richard; Schmid,Kira; Swick, Andrew; Joyal, Steven (2018), An open label study to evaluate the effect of Kaempferia parviflora in support of erectile function and male sexual health among overall healthy males 50–70, Federation of American Societies for Expiremental Biology, Volume 31, Issue S1
Special Issue: Experimental Biology 2017 Meeting Abstracts, https://doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.31.1_supplement.636.1
Lim, T. K. (2016), Eurycoma longifolia, Edible Medicinal and Non-Medicinal Plants Pages 250–276
Khanam, Zakia; Shwu Wen, Chew; Bhat, Irshad Ul Haq (2015), Phytochemical screening and antimicrobial activity of root and stem extracts of wild Eurycoma longifolia Jack (Tongkat Ali), Journal of King Saud University - Science, Volume 27, Issue 1, Pages 23-30
Kotirum S.; Ismail S.B.; Chaiyakunapruk N. (2015),
Efficacy of Tongkat Ali (Eurycoma longifolia) on erectile function improvement: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials,
Complementary Therapies in Medicine Volume 23, Pages 693-698, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2015.07.009
Moses , Lusia Barek; Bakar ,Mohd Fadzelly Abu; Mamat, Hasmadi, Aziz, Zaleha Abdul (2021), Unfermented Freeze-Dried Leaf Extract of Tongkat Ali (Eurycoma longifolia Jack.) Induced Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Lines Hindawi, Volume 2021, Article ID 8811236, https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8811236
Muhamad, Ayu S.; Ooi, Foong K.; Chen, Chee K. (2015), Effects of Eurycoma longifolia on Natural Killer Cells and Endurance Running Performance, International Journal of Sports Science, Volume 5(3) Pages 93-98
Nhan NH, Loc NH. (2017), Production of eurycomanone from cell suspension culture of Eurycoma longifolia , Pharmaceutical Biology Vol 55(1) Pages 2234-2239
Rehman SU, Choe K, Yoo HH. (2016), Review on a Traditional Herbal Medicine, Eurycoma longifolia Jack (Tongkat Ali): Its Traditional Uses, Chemistry, Evidence-Based Pharmacology and Toxicology , Molecules, Vol 21(3) Pages 331
Ruan, Jingya; Li, Zheng; Zhang, Ying; Chen, Yue; Liu, Mengyang; Han, Lifeng; Zhang, Yi; Wang, Tao (2019), Bioactive Constituents from the Roots of Eurycoma longifolia, Molecules, Volume 24(17), Pages 3157; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24173157
See, Kwan Li; Tan, Shu Ying; Hirata, Yoshiyuki; Chan, Lai-Keng; Nagaoka, Yasuo; Uesato, Shinichi; Boey, Peng Lim (2021), Biotic elicitation at different feeding time in cell suspension cultures of Eurycoma longifolia Jack, a valuable medicinal plant, for enhancement of cytotoxic activity of bioactive compounds against human colon cancer cell line, In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Plant, Volume 58, Pages15–27
Sitanggang, Bintang Riris; Prijanti, Ani Retno; Astuty, Hendri (2018), The Role of Pasak Bumi (Eurycoma longifolia Jack) Extract as an Antimalarial Agent Through the Mechanism of Antioxidant Specific Activity (Superoxide Dismutase, SOD and Catalase, CAT) in Plasmodium berghei-Infected Mice, Advanced Science Letters, Volume 24, Number 9
由 tongkatali.org
tongkataliorg3@gmail.com
2023 年 5 月 3 日更新







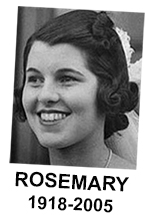




参考资料:

